Contracts play a critical role in regulating various aspects of our lives, both professionally and personally, and they are crucial to the functioning of modern society. With the advent of Blockchain technology, Smart Contracts have emerged as a game-changer, offering increased safety, security, and organization in transactions.
When talking about Smart Contracts, people also refers to them to as distributed apps. We could define them as an integral part of the ecosystem of platforms and applications that exist above the internet.


These self-executing agreements are stored and replicated on a Blockchain network and are designed to enhance the accessibility of applications running on these platforms. When specific conditions are met, the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller are automatically executed, without the need for intermediaries. But what exactly are Smart Contracts and what problem do they solve?
An Introduction to What’s a Smart Contract?
Have you ever wondered what lies behind the magic of decentralized systems? The answer is simple – smart contracts. A smart contract is a self-executing agreement stored on a blockchain network, powered by code and representing the terms of the agreement between parties.
The concept of smart contracts has been around since the late 1990s, but it wasn’t until blockchain technology emerged that they truly came to life. Web3 smart contracts automate the execution of transactions by meeting pre-determined conditions, making the outcome transparent and easily verifiable. The code is stored and executed on the blockchain, making the agreement immutable and decentralized.
In other words, smart contracts explained are computer programs or protocols that use if-then logic to execute automated transactions. The terms of the agreement between buyer and seller are inscribed directly into the code, ensuring a traceable, transparent, and irreversible transaction process.
The use of smart contracts meaning eliminates the need for intermediaries, reducing time delays and increasing efficiency. With the development of smart contracts, the concept of a fully automated world where code dictates what we can and cannot do is becoming a reality.


A Brief History of Smart Contracts
Smart Contracts have a rich history that dates back to the 1990s when computer scientist and legal scholar Nick Szabo first introduced the concept. The term “smart contract” was coined by Szabo refers to a set of promises in digital form.
He described the principle of smart contracts as digital protocols for information transfer that use mathematical algorithms to automatically execute a transaction once the established conditions are met, fully controlling the process.
Yes! Nick Szabo wrote the best definition of smart contract 28 years ago (He might actually be Satoshi Nakamoto.)
The advent of blockchain technology in 2008 with the creation of Bitcoin served as a catalyst for the development of smart contracts.
And despite Szabo’s groundbreaking work, the concept remained an abstract idea until the Frontier release of Ethereum in 2015, which marked the first implementation of smart contracts. This release brought smart contracts to life and sparked a new era of experimentation and exploration within the community.
The launch of the Ethereum network, the first ICO using smart contracts, and the increasing use of smart contracts around the world are just a few of the key events in the history of smart contracts.
Benefits and Advantages of Using Smart Contracts


The advent of smart contracts has changed the way transactions are conducted, providing a plethora of benefits in terms of speed, efficiency, accuracy, trust, transparency, security, and savings. To learn more about the various benefits of smart contracts, read on.
Increased Speed, Efficiency, and Accuracy
Processing documents manually is a time-consuming process and often leads to delays in achieving objectives. With the use of smart contracts, this process becomes automated and in most cases, does not require personal involvement, which saves valuable time. Transactions can be executed instantly and automatically, reducing the time and effort required for manual verification and intermediaries. This results in a more streamlined and accurate process, freeing up resources for other tasks.
What if they want to swap tokens on Sunday? With smart contracts, these kinds of problems go away. The contract can be fulfilled seconds after the initial criteria are met. Cost is another benefit of smart contracts compared to traditional contracts. Traditional contracts are not only expensive because of the intermediary that has to make a profit, but there is also a huge risk of hidden costs for things like arbitration and enforcement.


Greater Trust and Transparency
Trust and transparency are two important aspects of smart contracts. By eliminating intermediaries and third-party verification, smart contracts create a trust-based system that is secure and transparent. This reduces the risk of fraud and errors, and ensures that all parties involved in a transaction have access to the same information.
There’s no need to worry about information being tampered with for personal gain, as encrypted transaction logs are exchanged among participants. The guarantee for the transaction is the program itself, which is immune to interference, unlike middlemen who can introduce doubt about the integrity of the process. Smart contracts rule out the possibility for third-party interference, creating a secure and reliable system for conducting transactions.


Enhanced Security Measures
Security is a big deal when it comes to transactions, and smart contracts have got you covered!
The decentralized and automated nature of these contracts means no one can cheat the system or hack into it (or almost). The code of a smart contract is public for all to see, making it easy to track and verify transactions. Plus, the information entered in the blockchain stays there forever and can’t be changed or deleted.
So, if one person doesn’t hold up their end of the deal, the other person is protected by the conditions of the smart contract. And here’s the cherry on top – the records of blockchain transactions are encrypted, making them super hard to hack. In fact, if someone tried to change one record, they’d have to change the whole chain! All in all, smart contracts provide a secure and trustworthy way to conduct transactions.
Cost Savings
Savings, savings, savings! Who doesn’t love that? Well, with smart contracts, you can save big time.
By cutting out intermediaries and automating the verification process, smart contracts can help lower costs and boost efficiency across a wide range of industries. That’s right, from finance and insurance to real estate and logistics, smart contracts have the potential to create some serious cost savings and improve overall efficiency.
And because smart contracts eliminate expenses for middlemen and reduce operational costs, you’ll have more money in your pocket. It’s a win-win!
It’s no surprise that smart contracts are becoming a popular choice for businesses and individuals alike. So whether you’re looking to streamline your operations or ensure the security of your transactions, smart contracts are a powerful tool that you just can’t ignore.
With the benefits of smart contracts in mind, it’s natural to wonder how they achieve such efficiency and security. Let’s explore the mechanics behind this innovative technology.


How Do Smart Contracts Work?
Smart contracts operate by following simple ‘if/when…then…’ statements that are written into code on a blockchain network. This code is executed when predetermined conditions have been met and verified (as we mentioned earlier), resulting in actions such as releasing funds, registering a vehicle, sending notifications, or issuing a ticket.
To establish the terms of a smart contract, participants must determine how transactions and data are represented on the blockchain, agree on the governing rules, explore all possible exceptions, and define a framework for dispute resolution. The smart contract can then be programmed by a developer or by using templates and online tools provided by organizations that use blockchain for business.
Smart contracts can rely on purely blockchain-based information or an external data source, such as the Ethereum or S&P 500 price. However, the trust required for external data can be minimized through the use of Oracle services, like Chain Link, which provide accurate information. With the ability to implement their own smart contracts, blockchain projects like Hi-RIAM are revolutionizing the way agreements are made and executed.
Furthermore, smart contracts on Ethereum are decentralized, with no single machine controlling the contract. In fact, all nodes on the Ethereum network store the exact same contract with the same state.
The most common and widely used example to define what’s a smart contract
Think of a vending machine as an example of a smart contract. Just like a vending machine has rules for what happens when you insert money, a smart contract has rules set in code for what happens when certain conditions are met. It works in a fully deterministic way.
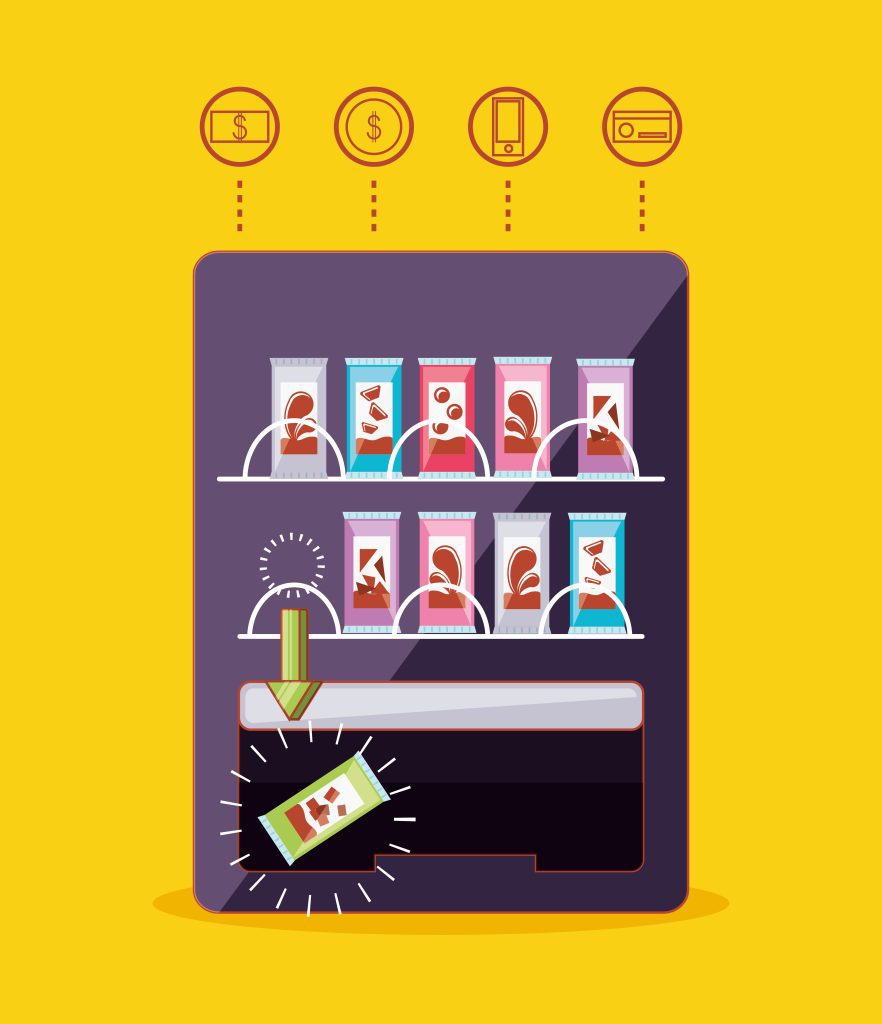


In this analogy, if you insert two dollars into a vending machine, you’ll get a can of coke. But if you only insert one dollar, the machine won’t give you the drink. On the other hand, if you insert three dollars, the machine will dispense the coke and return change in a predefined, programmed way, based on available coins and which coins the machine wants to prioritize dispensing first.
What are the major parts of a smart contract
The anatomy of a smart contract is crucial to understanding the potential of smart contracts on blockchain technology. The structure of a smart contract is made up of three major parts: database schema, validation and verification of transactions, and query optimization logic for reading the ledger.

These elements work together to ensure that the smart contract operates as intended and that the data stored within it is secure. The database schema defines the structure of the data stored within the smart contract, while the validation and verification of transactions is responsible for ensuring that the data being added or updated within the contract is valid.
Finally, the query optimization logic helps to accelerate the process of reading data from the ledger, making it more efficient. Smart contracts are stored on the blockchain and are open source, meaning that they are publicly accessible and can be reviewed and audited by anyone. This level of transparency is an important aspect of the trust and security that smart contracts bring to the world of transactions.

Use Cases of Smart Contracts on blockchain
Smart contracts on the blockchain have the potential to change the way we handle money and assets.
By automating transactions and enforcing agreements in a secure, transparent, and decentralized manner, smart contracts offer new opportunities in the digital world.
This section will take a closer look at how smart contracts are utilized in various applications, including digital wallets, the DeFi sector, the crypto industry, and NFTs.


Smart contract and digital wallets
Smart contract wallets, like Trust Wallet, are a prime example of the practical applications of smart contracts in blockchain technology. These wallets utilize the power of smart contracts to automate and secure transactions, making intermediaries a thing of the past and reducing the risk of fraud and hacking. This means that users can manage their assets with ease and peace of mind, knowing that their funds are always secure.
Let’s take a look at an example. Imagine you’re an investor and you’ve set a specific price point for an asset. With a smart contract wallet, you can program the wallet to automatically execute a transaction if the price of the asset reaches that point. For instance, if the asset reaches its target price, the smart contract could automatically sell it, ensuring that you get the maximum profit.
In a world where we’re becoming increasingly reliant on technology, it’s great to know that we can trust smart contract wallets to handle our assets with care.


The Rise of DEFI
Smart contracts and digital wallets go hand-in-hand in the world of DeFi (Decentralized Finance). DeFi is one of the hottest industries and it’s built on the backbone of smart contracts. One of the most innovative things being done with smart contracts in DeFi is the creation of decentralized stable coins.
For example, MakerDao allows for automated liquidity provisioning to create a stable coin that’s pegged to the US dollar, without actually storing dollars in the real world.


Imagine smart contracts as a recipe for a financial dish, where you mix different ingredients (tokens) to create a delicious and valuable meal. A decentralized exchange (like UniSwap or Kyber Network) allows you to trade tokens in a completely permissionless and decentralized fashion. With smart contracts, you can create a pool of money with two different tokens and write code that allows traders to switch from one token to another, adjusting the prices as one increases in volume.
It’s like being able to trade apples for coconuts (where apples and coconuts represent different tokens) just by following a set of rules written in the smart contract. This opens up new possibilities for day traders or investors looking to get into specific coins that aren’t on major exchanges like Coinbase.
The integration of DeFi with smart contracts is a game-changer for the world of finance and has the potential to democratize access to financial services for billions of people. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting out, DeFi is worth taking a closer look.


Smart Contracts in the Cryptocurrency Space
The utilization of smart contracts has proven to be particularly beneficial in initial token offerings, enabling companies to launch these offerings with greater efficiency and security. Transactions are executed as intended, reducing the risk of fraud and creating a more trustworthy experience for all involved.
Another major application of smart contracts in the cryptocurrency world is in decentralized exchanges. These exchanges leverage crypto contracts to automate and secure transactions, providing users with a more transparent and secure trading experience. The elimination of intermediaries, thanks to the implementation of smart contracts, reduces the risk of fraud and hacking, making the trading of digital assets a safer and more user-friendly experience.


Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) and Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are transforming the NFT landscape, providing new and innovative solutions for artists and creators to monetize their work. With smart contracts, NFTs can be created and managed with increased security and efficiency, reducing the risk of fraud and ensuring that all transactions are executed as intended. This makes the NFT market more accessible and secure, creating new opportunities for artists and creators.
For instance, an artist can create an NFT using a smart contract and set the terms for buying and selling it. The smart contract would then enforce these terms, ensuring the artist always receives a fair price for their work. This showcases the potential of smart contracts in the NFT market and how they are enabling new opportunities for the creative industry.
The creation of NFT marketplaces is also a great opportunity to demonstrate individual talents and creative artifacts and exhibit those products to inspire proper digital asset management. The process of NFT marketplace creation has a critical aspect of NFT smart contract development, which involves various exclusive features and development aspects. The integration of smart contracts in the NFT market has the potential to revolutionize the music industry and other creative sectors.
Best real-world examples of smart contracts
The potential of blokchain contracts is limitless, and we are only scratching the surface of what’s possible with this cutting-edge technology. But it’s not all theory – there are already numerous real-world examples of smart contracts being put into action, making a real impact in various industries.
Smart Contacts in Insurance
Did you know that you can bring an insurance company to life with just a few smart contracts? The concept is simple: let’s say farmer John pays us $2,000, and if the temperature exceeds 95°F for four consecutive days in Missouri, the smart contract will pay him $10,000. This is essentially insurance, where farmer John can be confident that in case his crops fail due to a heat wave, the smart contract will recognize the temperature change and compensate him for his $100,000 insurance.
But how does a smart contract, a piece of code, know about the temperature in Missouri? That’s where oracles come in – they’re tools that act as trusted sources of real-world information to anything on the blockchain that requests it.
And where does the initial $100,000 come from? Investors would have to pool their money together to start the insurance company and lock it up in the smart contract. The funds are inaccessible until the end of the summer when the smart contract owns the money.
In case the insurance isn’t paid out to farmer John, the initial investment plus his $2,000 premium get returned to the investors.
Smart contracts could be a highly profitable use case in the insurance industry, and the possibilities are endless!


Smart Contacts and Flight Insurance
Let’s consider a real-life scenario in which smart contracts are used. Imagine yourself stuck at the airport with a delayed flight. But, what if we told you that there’s a solution to this problem? Enter smart contracts.
AXA, an insurance company, has implemented the use of Ethereum smart contracts for their flight delay insurance. This insurance compensates you if the flight is delayed for more than two hours, as stated in the insurance policy.
Here’s how it works: The smart contract is linked to a database that records flight status and is created with specific terms and conditions. When the flight is delayed for more than two hours, the smart contract automatically executes and compensates the passenger, without any need for human intervention.
The smart contract is submitted to nodes on the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EMV) for evaluation, where all nodes must come to the same result. The result is recorded on the distributed ledger, ensuring that the agreement is immutable and cannot be altered by anyone. This innovative use of smart contracts in the insurance industry is making it easier and more secure for customers to receive compensation in case of flight delays.


Voting: a life-changing Implementation of Smart Contracts
The use of blockchain technology in voting processes can eliminate long-standing problems in traditional centralized voting systems. With them, issues such as identity fraud, vote miscounts, and bias by voting officials can be a thing of the past.
The smart contract sets predetermined terms and conditions that guarantee secure voting. Each voter casts their vote using their unique digital identity, ensuring that no one else can vote on their behalf. The voting process is also foolproof, with each vote recorded on the blockchain network and tallied automatically, reducing the risk of third-party interference or manual errors.
The validation of votes is done by the users on the blockchain network, and the information is recorded on a ledger that is publicly available for audit and verification. Smart contracts also give you the ability to customize voting systems by adding or removing members, changing voting rules, and altering the majority rule.
For example, you can create a vote for a decision within a decentralized autonomous organization where the outcome is determined by a voting mechanism within the organization, rather than relying on a central authority to make the final call.
Implementation of a Smart Contract in Crowdfunding
Implementation of a Smart Contract in Crowdfunding: Crowdfunding has become a popular way for entrepreneurs and product teams to raise funds for their projects.
Traditionally, this has been done through a third-party platform such as Kickstarter, where supporters trust the platform to handle their money correctly. However, with the implementation of smart contracts on blockchain technology, crowdfunding can now be automated and made more secure.
For instance, Ethereum-based smart contracts can be used to create digital tokens for transactions. Entrepreneurs can design and issue their own digital currency, creating a tradable computerized token that uses a standard coin API.
The contract can then be programmed to release funds only if a certain goal is met, providing added security for contributors. Additionally, the use of a Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) in the crowdfunding process eliminates issues with centralized management systems. Every contribution is recorded on the blockchain and terms and conditions are set in the contract, giving every participant a token.


The Role of Smart contracts in real estate
Imagine a scenario where instead of going through the traditional process of advertising the house, securing funding, using escrow, getting insurance, and closing, you could buy and sell a property just as easily as you would buy and sell a stock on the blockchain. The deed of the property would be stored on the blockchain and would be owned by whoever holds it, eliminating the need for banks or other intermediaries.
With smart contracts, you can send an offer on the blockchain and within minutes the other person can accept or reject. If they accept, you immediately own the new deed and the other person immediately receives payment, without the need for costly commissions and lengthy delays associated with traditional real estate transactions. Smart contracts have the potential to make buying and selling properties faster, easier, and more accessible, especially for those who are deterred by high fees or who want to avoid paying commissions to third-party companies, banks, lawyers, or house brokers.
Digital Identity
Digital Identity is one of the most promising use cases for smart contracts on blockchain technology. Our digital identity, which includes our data, reputation, and digital assets, is a crucial aspect of our lives.
With the help of smart contracts, we can securely and efficiently manage our digital identity, providing us with new opportunities while also ensuring that sensitive information remains private.
Smart contracts can allow other parties to verify transactions and obtain information about us without revealing our true identity. This frictionless approach to know-your-customer (KYC) verification can help improve security, compliance, and interoperability, making our digital identity more resilient and valuable.
For example, imagine a scenario where you could securely and easily apply for a loan, open a bank account, or access a new service, all with the click of a button, knowing that your digital identity is secure and accessible when you need it.


Earning money with smart contracts
Earning money with smart contracts is a unique and innovative way to take advantage of the power of blockchain technology.
What if we told you that you could borrow 10 million dollars with no money down? Well, on the Ethereum network, you absolutely can. But only if you write a smart contract that pays it back in the exact same minute that it is borrowed.
That’s right, you can borrow millions of dollars to do something for you on the Ethereum network if you know how to code it.
So here’s the catch, all of the money must be paid back.
You may be wondering why we would want to do this. Well, imagine you could buy some Dogecoin for 50 cents on Coinbase and then sell it for 55 cents on Gemini.
You could theoretically borrow 10 million dollars and buy a hige amount of Dogecoin on Coinbase and then sell it to Gemini and then pay back the original loan of 10 million dollars with some interest. This is called a flash loan, and some guy made 360,000 in a few minutes by creating one of these.
This is possible because smart contract can check itself. It can run a simulation of what you programmed and it can see if what you told it to do would actually be achievable. In short it would check if it’s able to pay back the lender.
If it can immediately pay back the lender, it runs the code and you can borrow those funds to do whatever you want to do. You could never do this with traditional finance, but you can on the blockchain.


Smart contracts and Lawyers
This technology is broadening the access to legal services with some smart contracts legally binding users around the world. By this, we can’t assure if smart contracts will replace layers, but there is a necessity to break the monopoly lawyers have in this space.
There is no reason for 90% of what lawyers do to be done by lawyers. For example, when you buy a house and you need a lawyer to sign documents, you might wonder why. The reason is because the law has been written to require this, but the people who benefit from this have corrupted the law. There is a lot to clean up.
However, if we can clean it up, then 99% of these tasks should be automated. Lawyers should focus on the difficult cases rather than everything that can be automated. This should be true not only within a jurisdiction but across jurisdictions.


The Reality of Legal & Regulatory Environments
The reality of the legal and regulatory environments surrounding smart contracts highlights the importance of lawyers in the crypto industry.
While it’s unlikely that lawyers will be completely replaced by code in the near future, they can provide valuable knowledge that can be translated into code.
And one of the most important innovations in the law industry, like in the Berkman Center and other organizations in the legal industry, are trying to push into the legal environment. They insist that just like lawyers now all study economics (because that’s a core way of thinking about the law) they also should study basic code. This way, they can effectively address the regulatory challenges in the web3 sphere.
So, this is the most important innovation that’s got to happen in the law. Lawyers have to become technically sophisticated to be able to read code like they read legal contracts. They must have a conceptual understanding of what code can do, so they can think creatively about it like they think creatively about language.
Limitation and drawbacks of Smart Contracts
One major issue is scalability, where the increasing number of transactions on the blockchain results in longer wait times and higher transaction fees. This can make it difficult for businesses and individuals to use smart contracts effectively, especially in industries where transactions need to be processed quickly and efficiently. However, developments such as sharding and proof-of-stake algorithms show promise in mitigating scalability challenges.
Interoperability is another challenge facing smart contracts, as different blockchains have different programming languages and security protocols, making it difficult for them to interact with each other. This can limit the growth and adoption of smart contracts and make it challenging for businesses to adopt the technology across different platforms.
Moreover, the lack of regulation in the international legal field for blockchain, smart contracts, and cryptocurrencies can pose a challenge. The implementation of crypto contracts also often requires significant time, money, and effort.
Additionally, once a smart contract is deployed, it cannot be changed, which can be seen as both a pro and a con.
It is important to note that smart contracts are only as secure as the code they are built on. If a bug or security vulnerability is found in the code, it can lead to serious consequences such as theft of funds or loss of data. Therefore, thorough testing and auditing of the smart contract code before deployment is essential.
Despite these limitations, blockchain contracts have the potential to greatly improve efficiency, trust, and security in a wide range of industries. As the technology evolves, it is likely that these limitations will be addressed, leading to even greater adoption of smart contracts in the future.


The Sustainability of Smart Contracts
The sustainability of smart contracts is becoming a growing concern as the use of public blockchains has a significant carbon footprint and its impact on the environment is a matter of concern.
As technology leaders strive to address the problems and disadvantages of smart contracts, they must consider ways to decrease the environmental impact of public blockchains. On the other hand, enterprise blockchains tend to use fewer computational resources and with proper maintenance, can help maintain a low environmental impact.
It is imperative for technology leaders to consider sustainability and explore ways to reduce the carbon footprint of their smart contract projects. By being mindful of these environmental issues, the industry can ensure that smart contracts continue to drive efficiency, trust, and security while also reducing their impact on the environment.


Smart contract vulnerabilities
Smart contracts offer many benefits but are not immune to security vulnerabilities. It’s crucial to understand the potential dangers when using smart contracts.
Two of the main vulnerabilities of smart contracts include hacking and errors in the contract code.
Hacking: is a significant concern in the smart contract industry, especially in cryptocurrency where large amounts of money are at stake. Smart contracts, being computer programs, are susceptible to hacking just like any other software.
Hackers can exploit vulnerabilities in the smart contract code to steal funds or manipulate data. Although the use of computational logic to move data between nodes is one of the strengths of blockchain technology, bad actors have found ways to exploit the software’s interoperability.


Smart Contract Errors: in the smart contract code, one single error can lead to unintended consequences and potentially significant financial losses. For example, an error in the code of The DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization) led to the theft of $50 million in Ether in 2016.
The Ethereum community has since taken extra security measures such as security audits and formal verification methods to ensure smart contract security. However, even if a smart contract is bug-free and audited, there’s no guarantee that changes to the platform won’t cause problems.
Smart contracts must be well-written, secure and audited to avoid security risks. There are also legal and regulatory risks involved with smart contracts, which should be taken into consideration.









