Embarking on a trading journey introduces you to a world full of exciting opportunities and challenges. It’s a universe of numbers and strategies, where two terms hold vital relevance – the bid-ask spread and slippage. These terms aren’t just industry jargon; they’re pivotal pillars that determine the course of any trade, thus making them essential concepts for all traders. The bid-ask spread represents the cost of trading, while slippage demonstrates market volatility’s tangible impact. Whether you’re a novice trader making your first foray into trading or a seasoned professional fine-tuning your strategy, understanding these concepts can make a significant difference to your trading endeavors.
Understanding Bid-Ask Spread
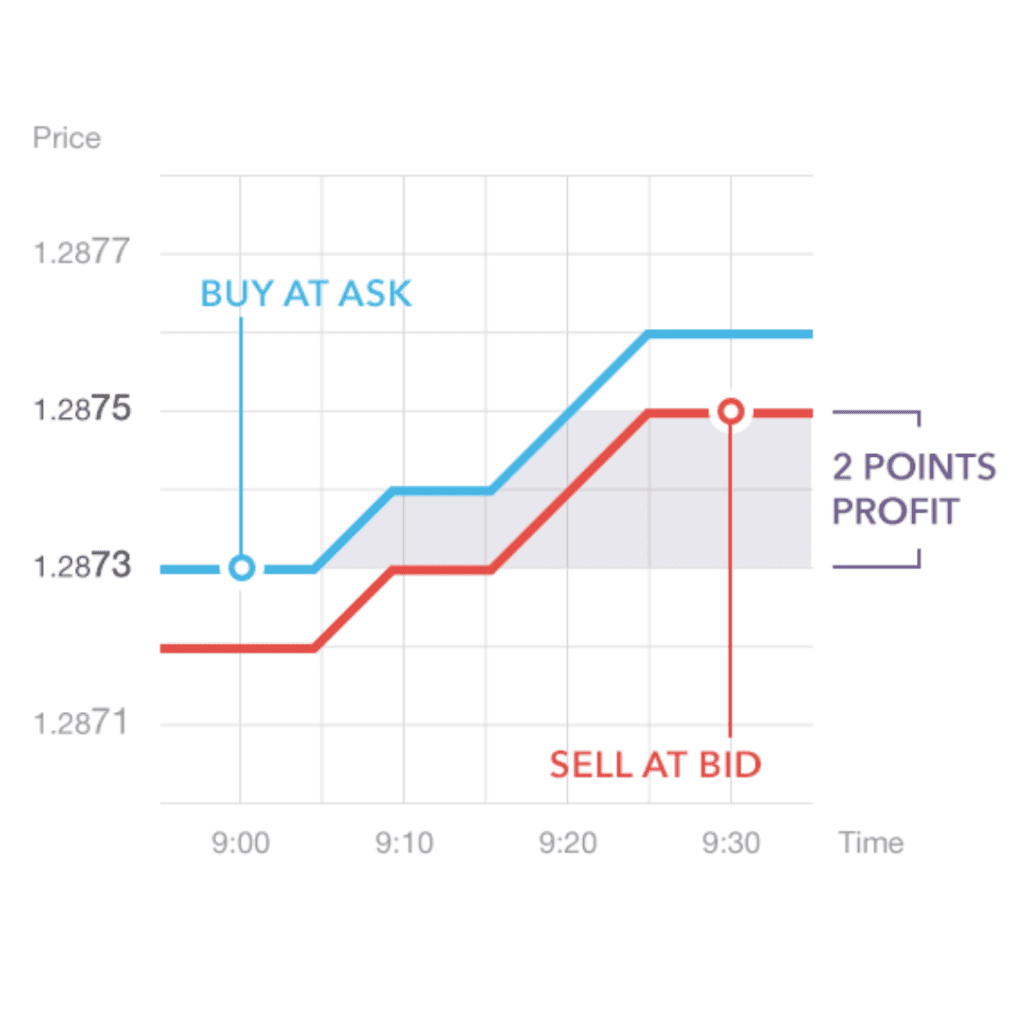

Diving into the world of trading, one of the first concepts to understand is the bid-ask spread. But what does it really mean? Well, imagine you’re in an auction. The ‘bid’ is the highest price that someone is willing to pay for an item. The ‘ask’ is the lowest price at which a seller is willing to part with the same item. The difference between these two prices is known as the bid-ask spread.
When it comes to trading, the bid-ask spread plays a fundamental role. Whether you’re dealing with stocks, bonds, or delving into “what is spread in cryptocurrency trading”, the principle remains the same. It’s the numerical difference between the bid price (the highest price a buyer is willing to pay for a security) and the ask price (the lowest price a seller is willing to accept for that same security). For instance, if the bid price for a cryptocurrency is $100, and the ask price is $102, then the bid-ask spread is $2. This spread is the transaction cost, which traders have to overcome to achieve profitability. Understanding this concept is essential as it forms the backbone of financial transactions and provides key insights into market liquidity and trading costs.
Unpacking Slippage: An Integral Part of Trading
Now, let’s explore another fundamental trading concept – slippage. Slippage refers to the change in the price of a security between the time the order is placed and when the order is executed. It’s the difference between the expected price of a trade and the price at which it’s actually executed. This can be the result of sudden market movements affecting the security’s price in the interim period.
To put it into context, suppose you place an order to buy a crypto coin at $300. But due to rapid fluctuations in market conditions, the price rises to $305 by the time your order gets executed. This discrepancy of $5 between the expected and execution price is the slippage you experience. While slippage isn’t confined to cryptocurrencies, the high volatility in crypto markets has led to frequent discussions about “slippage in crypto.”
In essence, slippage is an indicator of the market’s volatility and liquidity. Though it may sometimes lead to unexpected losses, it can also result in unexpected gains when the price moves in your favor. A comprehensive understanding of slippage is crucial for any trader, as it equips them to handle rapid market movements and fine-tune their trading strategies accordingly.
The Interplay between Bid-Ask Spread and Market Liquidity
The bid-ask spread isn’t just a simple difference between two numbers; it also provides vital insights into the liquidity of a market. Market liquidity is a measure of the ease and speed with which a security can be bought or sold in a market without affecting its price. A tighter (smaller) bid-ask spread signifies a more liquid market, while a wider (larger) bid-ask spread indicates lower liquidity.
In a liquid market, the frequent buying and selling of securities cause bid and ask prices to be continuously updated, resulting in a narrow bid-ask spread. Conversely, in an illiquid market, there are fewer market participants and securities are traded less frequently. This results in less competition among buyers and sellers, leading to a larger bid-ask spread. Therefore, understanding the bid-ask spread is crucial when considering “bid ask spread liquidity,” especially in volatile markets like cryptocurrency trading.
Tools for Evaluating Liquidity: Order Book and Order Depth
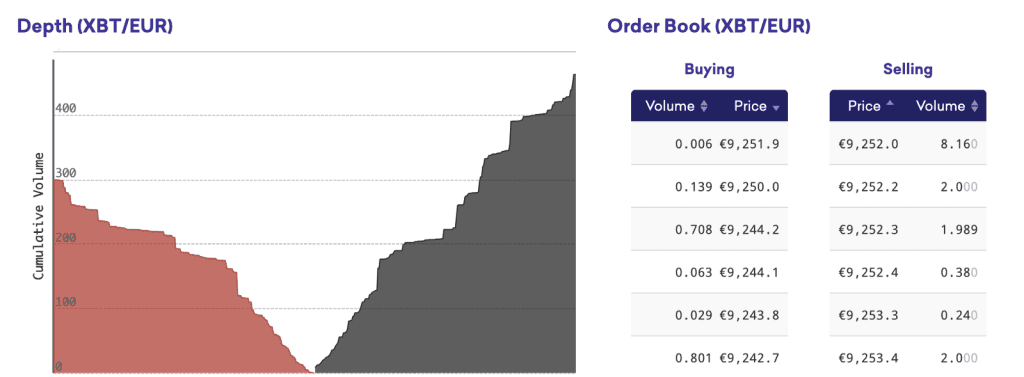
When it comes to evaluating market liquidity, two indispensable tools are the order book and order depth. An order book is a dynamic, real-time list of buy orders (bids) and sell orders (asks) for a specific security. It provides transparency into the market’s buying and selling interest, enabling traders to understand the supply and demand for a given security at various price levels.
On the other hand, order depth refers to the market’s ability to sustain relatively large market orders without impacting the price of the security. It’s directly related to the order book, as a deeper order book indicates high liquidity. Understanding these tools is crucial for every trader, as they provide insight into market sentiment and help forecast short-term price movement.
The Impact of Liquidity on Traders and Exchanges
Market liquidity significantly influences both traders and exchanges. For traders, liquidity directly affects the speed and ease with which they can execute their trades. High liquidity enables traders to quickly enter or exit positions without causing significant price changes, minimizing potential slippage. It also results in tighter bid-ask spreads, thus reducing transaction costs.
For exchanges, liquidity is equally crucial. A liquid market attracts more participants as it allows them to trade larger volumes without significantly affecting prices. This increased trading volume can lead to higher revenues for crypto exchanges in the form of transaction fees. Furthermore, a liquid market is often associated with less price volatility, providing stability to both traders and exchanges. Therefore, understanding the importance of liquidity is crucial for anyone involved in trading, as it plays a pivotal role in defining market dynamics and the profitability of trades.
How to Calculate the Bid-Ask Spread Percentage


To gauge the bid-ask spread in a more normalized and comparable format across different securities, traders often express it as a percentage of the mid-price (the average of the bid and ask prices). The formula for calculating the bid-ask spread percentage is as follows:
Bid-Ask Spread Percentage = (Ask – Bid) / Mid-price * 100%
Let’s take an example. Suppose we have a bid price of $100 and an ask price of $102. The mid-price would be $101 ($100+$102 divided by 2). The bid-ask spread percentage would be calculated as (($102 – $100) / $101) * 100%, which equals roughly 1.98%.
This percentage is a useful measure for investors because it helps them understand the cost of trading a specific security. The lower the percentage, the lesser the trading cost, which is especially crucial when dealing with large volumes or frequent trading.
How Often Does Slippage Occur in Trading?
Slippage is a common phenomenon in trading, and its occurrence depends on market conditions and the type of order used by a trader. In fast-moving markets, or when a large order is placed in a low liquidity market, slippage is more likely to occur. For example, slippage often occurs during periods of high volatility, when market orders are used, and also when large orders are executed.
In cryptocurrency trading, due to the market’s volatility, slippage can happen quite often. It’s essential to note that while slippage can lead to losses when the execution price is worse than expected, it can also lead to gains if the market moves in favor of the trader after placing the order but before its execution.
Understanding the conditions under which slippage occurs and developing strategies to minimize its impact can make a significant difference in trading outcomes, whether one is dealing with traditional assets or cryptocurrencies.
The Two Sides of Slippage: Positive and Negative

As the old saying goes, every coin has two sides, and so does slippage. Slippage can either be positive or negative, depending on the direction of the price movement.
Positive slippage occurs when the execution price is better than the initially expected price. For example, if you place a market order to buy a cryptocurrency at $100, but it gets executed at $98, you’ve experienced positive slippage. You got a better deal than initially expected!
On the flip side, negative slippage happens when the execution price is worse than the expected price. Using the same example, if your buy order gets executed at $102 instead of $100, you’ve encountered negative slippage. In this scenario, you’ve paid more than what you had intended.
Strategies to Minimize Slippage in Trading
Although slippage is inherent in trading, certain strategies can help you minimize its potential impact:
- Use limit orders: A limit order allows you to specify the maximum price you’re willing to pay when buying, or the minimum price you’re willing to accept when selling. This strategy provides protection against negative slippage but might result in missed trading opportunities if prices move unfavorably.
- Trade during peak hours: Market liquidity tends to be higher during peak trading hours, which reduces the chance of slippage. For global markets like forex or cryptocurrencies, it’s essential to identify these periods.
- Order splitting: For larger orders, splitting them into smaller chunks can prevent significant market impact and reduce slippage.
- Patience: Sometimes, waiting for the right market conditions can save you from negative slippage. If the market is too volatile, it may be wise to wait until it settles.
Conclusion
Understanding the bid-ask spread and slippage is crucial for any trader, irrespective of the asset class – be it stocks, forex, or cryptocurrencies. These elements can greatly affect your trading performance and outcomes. By understanding these concepts, and the impact of market liquidity on them, traders can make more informed decisions and develop strategies to minimize potential trading costs and slippage.
Remember that while the bid-ask spread represents a tangible cost of trading, slippage, being unpredictable, can work either in your favor or against you. With careful strategy and consideration, however, it’s possible to navigate these trading waters with confidence. Keep in mind the strategies we’ve discussed to minimize slippage, stay informed, and you’re well on your way to becoming a more efficient and effective trader!









